
Single cell RNA-Seq analysis
NextGenSeek offers cutting-edge single-cell RNA-Seq analysis to uncover cellular heterogeneity, rare subpopulations, and hidden biological insights. Transform your research today!
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is a revolutionary technology that has transformed our understanding of gene expression at the individual cell level.
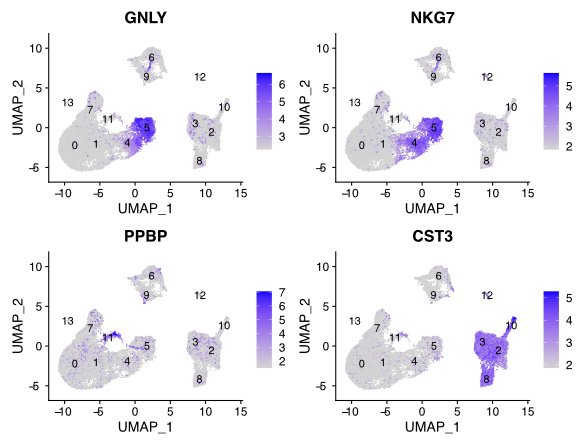
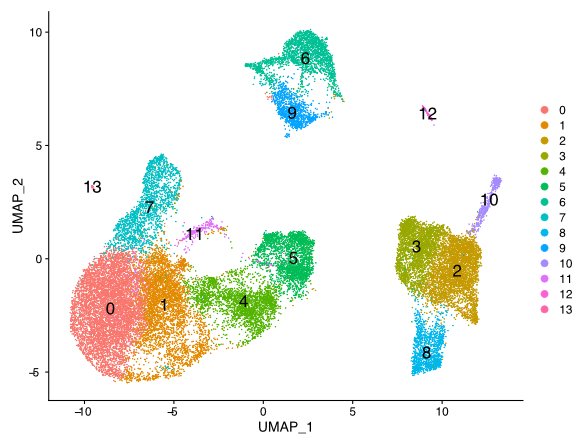
Compare gene patterns between cell types
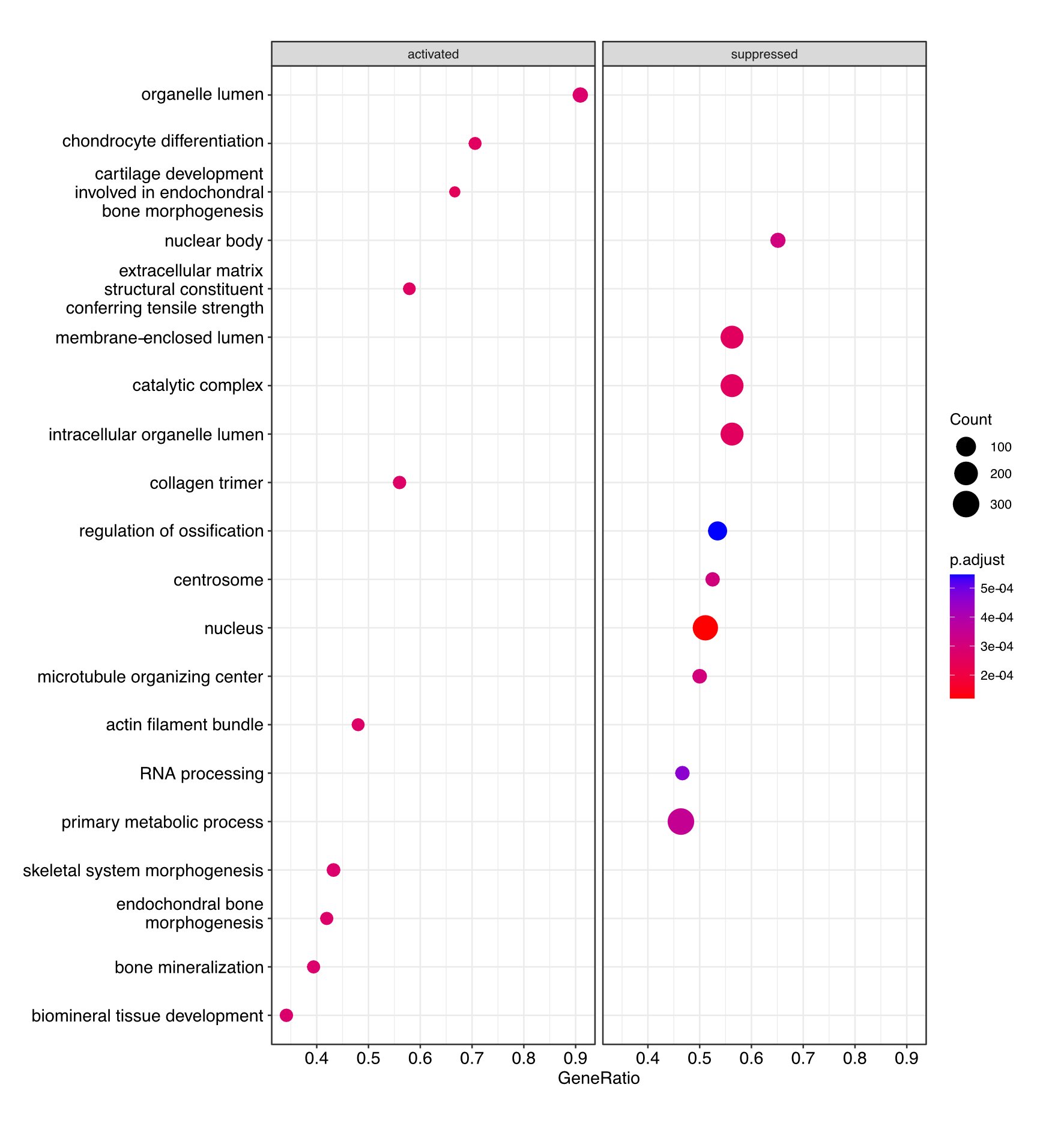
Dot plot image showing the most significantly activated and suppressed pathways
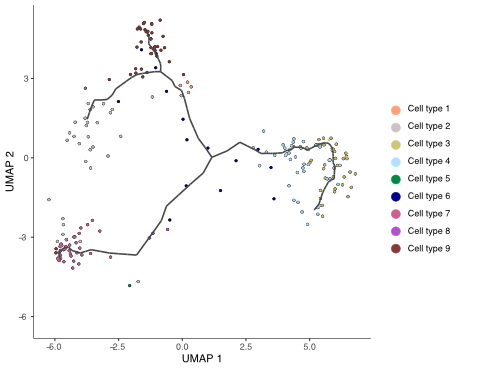
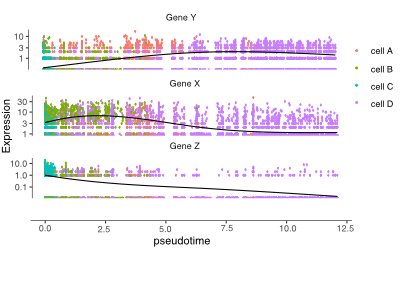
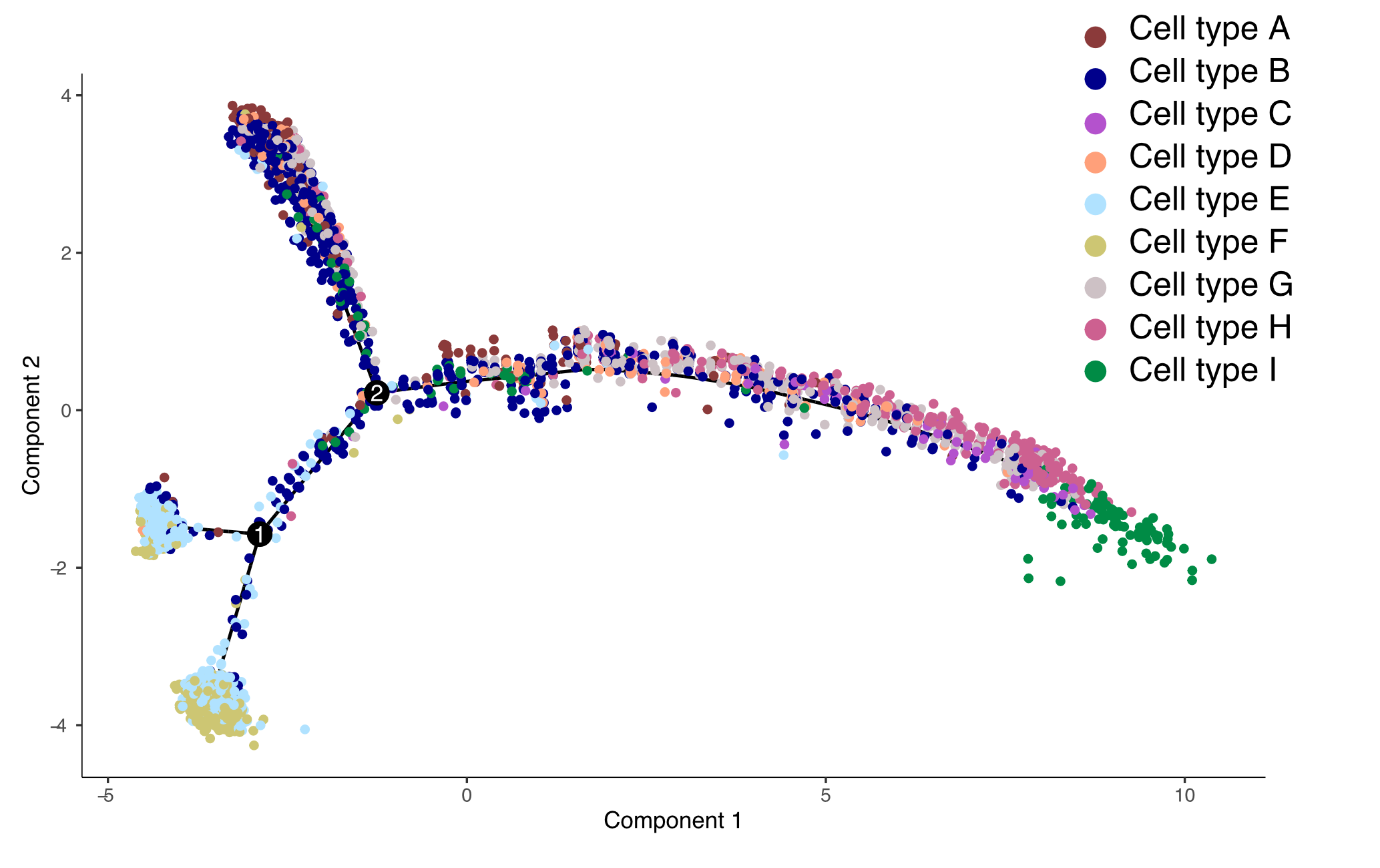
pseudotime
Conventional RNA-seq analysis, conducted on bulk RNA, provides valuable insights but cannot reveal interactions between different cells within a complex biological system. To address this limitation and obtain a high-resolution view of cell-to-cell variation, researchers turn to single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), which analyses the transcriptome of individual cells.
Key steps involved in scRNA-seq include:
Cell isolation: Individual cells are isolated from tissue samples using micromanipulation or microfluidic devices.
Library preparation: The RNA from each cell is isolated and fragmented, and adapters are added for subsequent sequencing of RNA molecules.
Sequencing: The cell-specific RNA libraries are then sequenced using NGS technology, typically Illumina sequencing.
Data processing: The sequencing data is processed to align the reads to a reference genome and to count the number of reads that map to each gene.
Data analysis: The data is analysed to identify gene expression patterns across different cell types and to cluster cells based on their unique gene expression profiles.
scRNA-seq has many applications, from development studies to investigating diseases and drug responses. It enables the identification of rare cell populations, exploration of cell-to-cell variability, and the discovery of novel cell types and subpopulations. The technique also examines transcriptomic changes in response to treatments, environmental changes, or disease states at the single-cell level.
Single-cell RNA-seq is a sophisticated and technical method requiring specialised equipment, software, and expertise. Additionally, the interpretation of scRNA-seq data demands a profound understanding, given its complexity and potential genetic variations within the data.
